Particle size analysis particle size measurement or simply particle sizing is the collective name of the technical procedures or laboratory techniques which determines the size range and or the average or mean size of the particles in a powder or liquid sample.
Laser particle size analyzer principle.
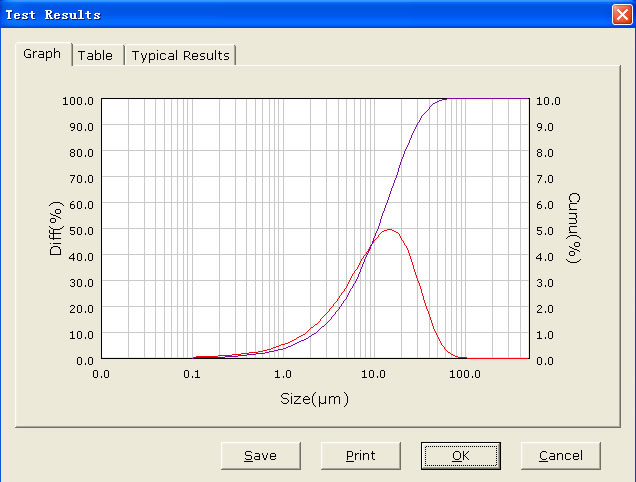
The basic workflow of a laser diffraction particle size analysis breaks down.
In fact the analyzer itself does not measure particle size it measures the angle and intensity of light scattered from the particles in your sample.
Ls 13 320 particle size analyzer.
The role of laser diffraction in particle analysis.
This process does not depend on volumetric flow rate the amount of particles that passes through a surface over time.
The ls 13 320 offers the highest resolution reproducibility and unsurpassed accuracy.
Malvern panalytical s unique practical laser diffraction particle size analysis know how enables the mastersizer to deliver results you can rely on with data quality analysis that empowers both particle sizing experts and measurement novices to deliver insight and results you can trust.
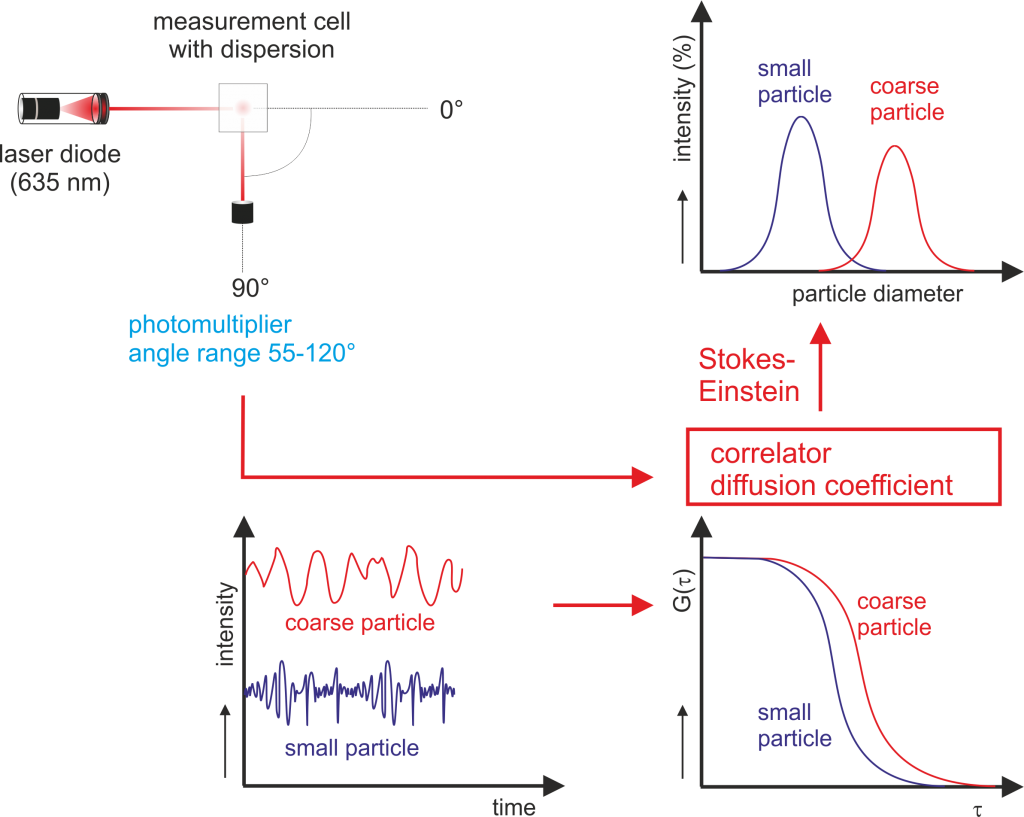
The light scattered by the particles at various angles is measured by a multi element detector and numerical values relating to the.
Discover the basic principles of particle size analysis here.
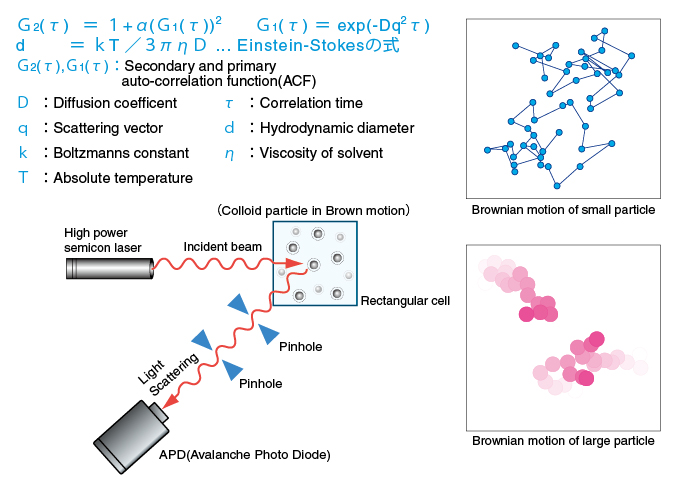
Laser diffraction measures particle size distributions by measuring the angular variation in intensity of light scattered as a laser beam passes through a dispersed particulate sample.
Laser particle size analyzer principle.
Particle size analysis is used to characterise the size of particles in a given sample.
Laser diffraction analysis also known as laser diffraction spectroscopy is a technology that utilizes diffraction patterns of a laser beam passed through any object ranging from nanometers to millimeters in size to quickly measure geometrical dimensions of a particle.
Particle size analysis is part of particle science and its determination is carried out generally in particle technology.
A representative sample dispersed at an adequate concentration in a suitable liquid or gas is passed through the beam of a monochromatic light source usually a laser.
Every analyzer from the very first commercial prototype to the state of the art la 960 utilizes this principle.
Over the last twenty years laser diffraction has to a large extent replaced traditional methods of particle size analysis such as sieving and sedimentation a previously common practice for granular material.
View the malvern panalytical mastersizer here.
Large particles scatter light at small angles relative to the laser beam and small particles scatter light at large angles as illustrated below.









.jpg)



