In addition to the argon ion laser 488 and 514 nm and the hene laser 543 nm another argon laser 364 nm was added to the microscope.
Laser scanning confocal microscope magnification and resolution.
Embryos and construct 3 d structures from the obtained images.
Capturing multiple two dimensional images at different depths in a sample enables the reconstruction of three dimensional structures within an object.
Images led to a growing interest in confocal microscopy 20.
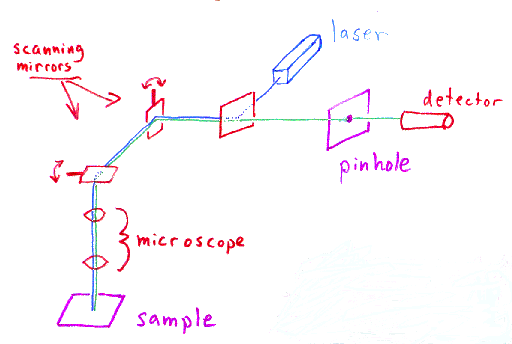
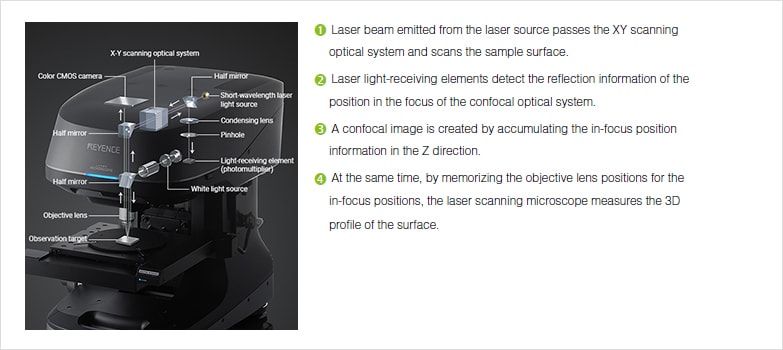
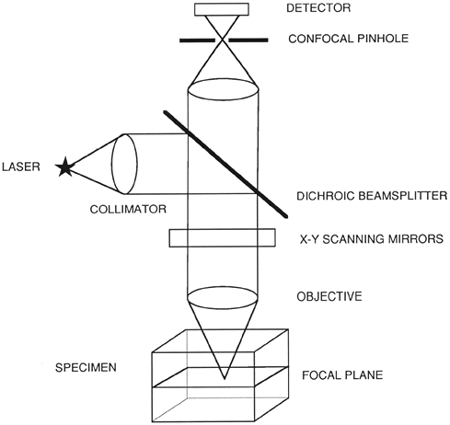
Laser scanning confocal microscopy laser scanning confocal microscopes employ a pair of pinhole apertures to limit the specimen focal plane to a confined volume approximately a micron in size.
Light microscope transmission electron microscope scanning electron microscope and laser scanning confocal microscope.
This technique is used extensively in the scientific and in.
4 x 1 to 2048 x 2048 pixels.
A the use of microscopy to observe and investigate different types of cell and cell structure in a range of eukaryotic organisms to include an appreciation of the images produced by a range of microscopes.
In the confocal laser scanning microscope the highest frequency to be sampled f is imposed by the optical system and for a particular resolution specification.
A zeiss confocal scanning laser microscope lsm 10 uv carl zeiss oberkochen germany has been adapted for uv fluorescence confocal microscopy kapitza wilke 1988.
With confocal laser scanning microscopy clsm we can find out even more.
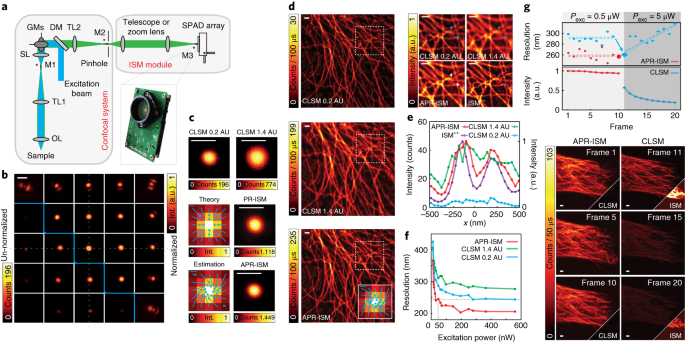
Confocal microscopy most frequently confocal laser scanning microscopy or laser confocal scanning microscopy is an optical imaging technique for increasing optical resolution and contrast of a micrograph by means of using a spatial pinhole to block out of focus light in image formation.
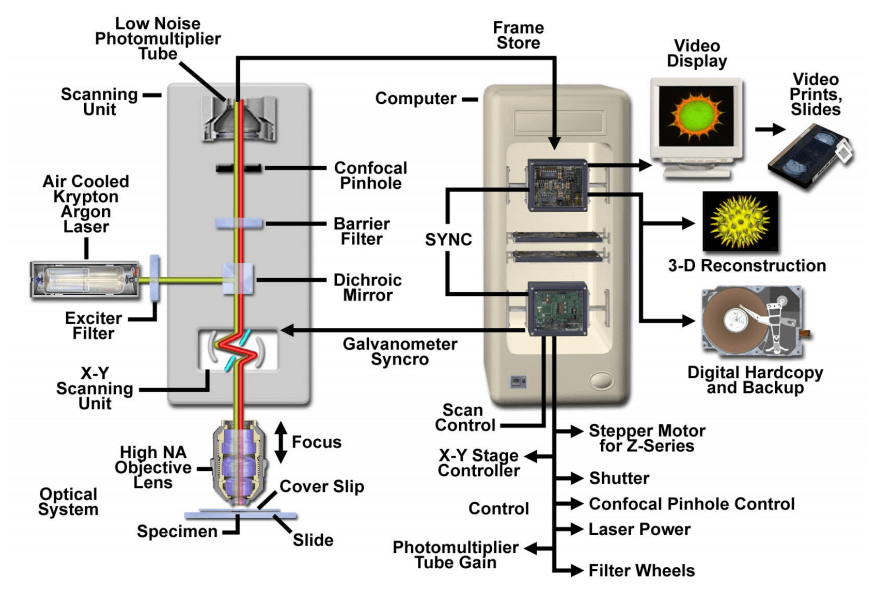
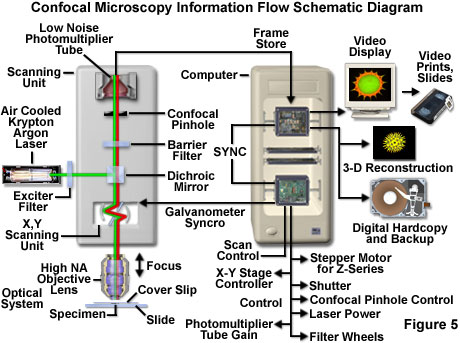
Relatively thick specimens can be imaged in successive volumes by acquiring a series of sections along the optical z axis of the microscope.
Lsm 700 confocal laser scanning microscope for materials analysis.
F 1 r resolution.
Masters et al 1991.
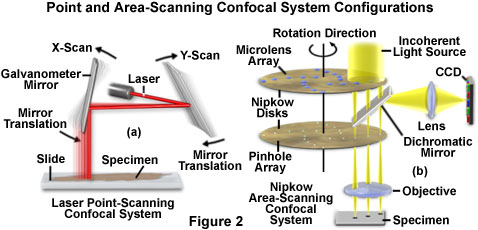
In laser scanning confocal microscopy the image of an extended specimen is generated by scanning the focused beam across a defined area in a raster pattern controlled by two high speed oscillating mirrors driven by galvanometer motors.
Fred brakenhoff developed a scanning confocal microscope in 1979 21.
The entire depth of the specimen over a wide area is illuminated by the widefield microscope while the sample is scanned with a finely focused spot of illumination that is centered in the focal plane in the confocal microscope.
Clsm combines high resolution optical imaging with depth selectivity which allows us to do optical sectioning.