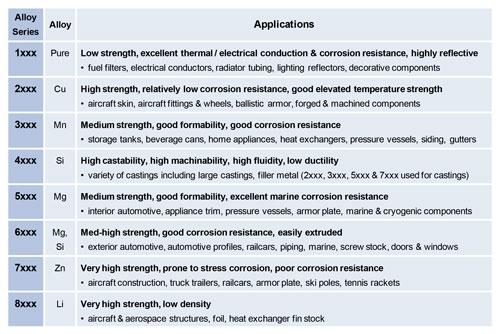
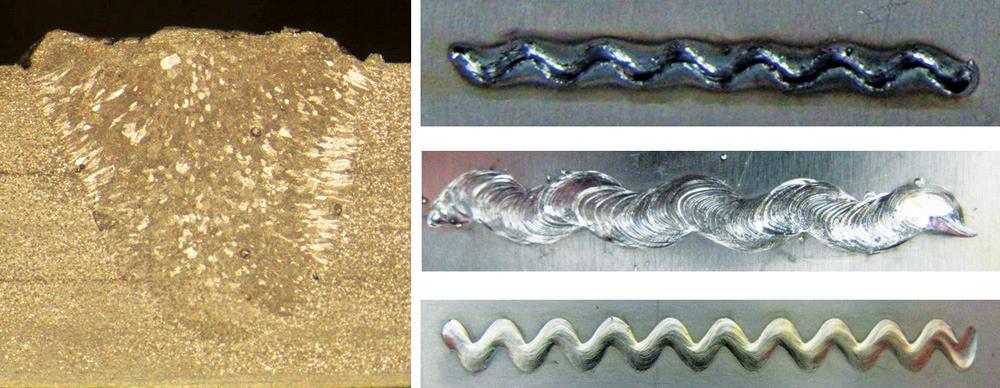
Laser beam welding can be used with crack sensitive materials such as the 6000 series of aluminum alloys when combined with an appropriate filler material such as 4032 or 4047 aluminum.
Laser welding aluminium problems.
The laser wavelength is 1 06 micrometers or less and a single 8 millisecond pulse is used.
There are several different types of lasers that work well with aluminum and often the use of a cover gas is prudent.
However with the evolution of high power good beam quality carbon dioxide co 2 lasers and the advent of high power high brightness solid state fiber delivered lasers coupling the energy into aluminum is no longer an issue.
Laser welding problem of aluminum alloy 1.
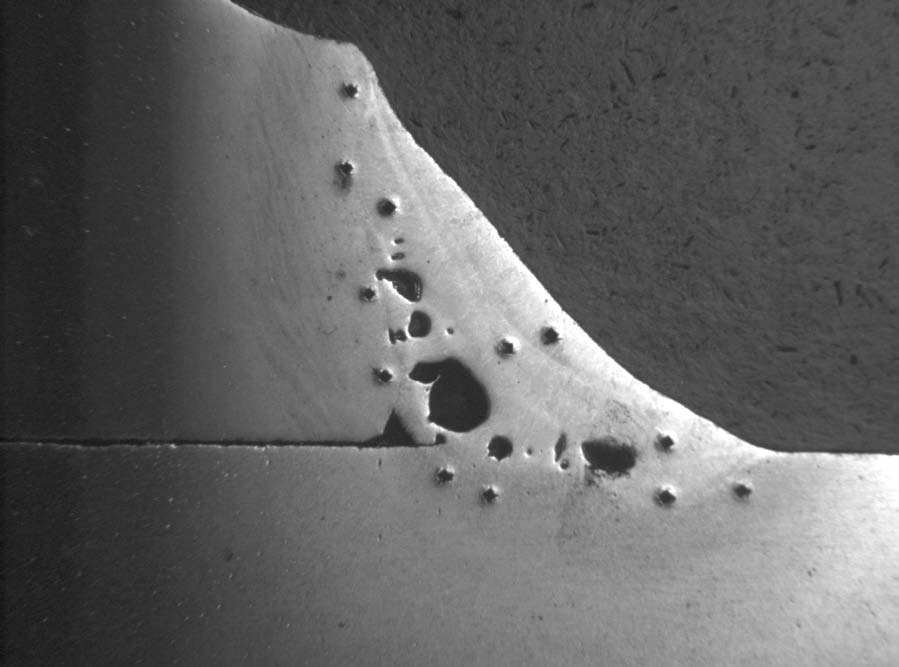
Porosity in laser welds can be caused by plate.
In the past aluminum s high reflectivity was a problem for laser welding.
The problems linked to the welding of components having large thicknesses were examined in this work while referring to the operative parameters and analysis of the types of defects both internal and external that were encountered when setting up and in the laser co2 welding of these components.
Because of the high initial reflectivity of aluminum alloy to laser beam and its high thermal conductivity the absorption rate of aluminum alloy to laser beam before melting is very low.
This problem is mainly due to the problem of aluminum alloy material.
The likelihood of laser welds to suffer solidification cracking can limit the welding speed parent material composition or weld penetration depth that is possible when laser welding both steels and aluminium.
Low absorption rate of aluminum alloy to laser.
Porosity is a less critical defect in laser welds than solidification cracking.
In this review the available research on the laser welding of 5xxx 6xxx and some 2xxx series automotive aluminium alloys is critically examined and interpreted from different perspectives.
Copper and aluminum conductors are butt welded or corner welded by a two part process involving heating and melting the cu al interface with energy from a pulse laser and simultaneously generating a contact pressure.
This form of cracking in aluminum is typically caused by a combination of metallurgical weaknesses of the weld metal as it solidifies with transverse stress applied across the weld.
Laser conduction welding lcw 10 6 w cm 2 is comparatively stable and may offer an alternative means of welding traditionally difficult materials such as aluminum alloys.
A problem that can be easily encountered when aluminum welding is solidification cracking or the hot cracking problem.
The laser induced plasma can influence the keyhole stability and thus the problem of keyhole porosity is more serious in co 2 laser welding than in yag and fiber laser welding.